Posts
Showing posts from October, 2016
Analysis of a Movie Clip
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Now You See Me- The Piranha Tank The clip above introduces one of the protagonists the the audience, giving them a first impression. The impression that we get is that she is daring and is willing entertain people, even if her life is at risk. This suggests that she is passionate at what she does, and likes to trick people, as later on the scene she makes everyone believe that her trick went wrong and that she died. However, she yelled from the crowd after that the act was a sick joke, showing humor herself, as well as amusing and relieving the audience. We can also get a sense of the character from her looks and outfit; her hair is a bright orange/red and her outfit is quite revealing, which indicates that she is confident in what she does and may not care what others think. Stereo-typically, the male character is quite dominating and always faces danger, however this clips contradicts that, showing that there can be a strong female lead. Moreover, later on in the clip we learn ...
Camera Movement (3)
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Focus-Pull Focus Pull- This occurs when you change focus throughout the scene, e.g. from the foreground to the background. This gives the effect to the audience that whatever is being pulled into focus is significant, and draws their attention to it, and if something is going out of focus, then it is longer the subject of the shot. Dolly Shot- Also known as a tracking shot, this involves having the camera on a trolley, which will move along to follow a subject. This is commonly used for POV shots and long takes, where the audience will feel involved in the scene, as they may feel that they are being taken somewhere
Camera Movement (2)
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Tilting Tilting up/down- This shot involves the camera moving up an down, for example in a POV shot to show that the subject is nodding. However, this technique isn't as common as panning, because humans look left and right more often than up and down. This shot can also be used to show other subjects/objects or even just the environment, for example if there is something on the floor or in the sky high up. Arc Shot- This shot is when the camera circles the subject(s), typically in an action film or a scene that is meant to create drama and suspense. This is used to give the subject power, usually just after they have achieved something or just before the climax in the film, for example a fight scene. Cut away/in (Camera Movement) Cut away shot- This is a shot of something other than the subject/action, which can add interest and information to the story, so the audience can focus on something other than the subject. Cut in shot- This is the opposite of the...
Camera Movement (1)
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
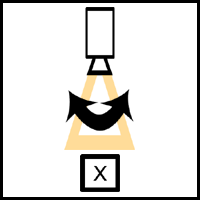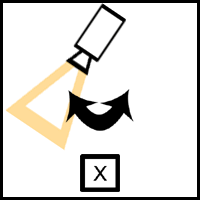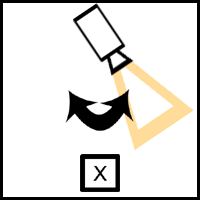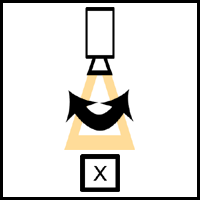
Pan Shots Pan shot- This shot is used to make the camera look left to right, for example, in a scene where we are following the subject. A steadicam can be used to get a smooth or professional shot, or it can even be handheld , especially during a POV shot to make it look more realistic. Its is the most simple and common method of camera movement, and is often used to do a sweep of an environment, which can set the scene and introduce it to the viewer. Whip pan- This shot is similar to the pan, however it is faster so that it gives a blurred effect. It is commonly used as a transition between shots, and can express a change in time or scene. It can also be frequently seen in cartoons, often accompanied by a 'whoosh' sound effect. Zoom Shots Zooming in/out- This does not require the camera to move, but it creates the illusion that it is further/closer to the action or subject. Zooming in can hold emphasis on a particular char...
Camera Movement Introduction
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Camera Movement Camera movement can function in many ways, it can direct the viewer's attention and reveal off-screen space and the subject's surroundings. This technique is used typically when the subject is moving across the frame, so it is used as a following shot. The shot shown on the left is an arc shot, which circles the subject(s). Each shot can connote something or give the subject a sense of something, for example power. Example shots include: Pan shot, whip pan, tilt, dolly-shot. arc shot, zoom in/out, pull focus, handheld, steadicam and cut away/in shot (also counts as part of camera framing) The video explaining camera framing also explains briefly some of the camera movements: Start from 1:40 Here is another video with example camera movements: